Physical Characteristics: Mercury Vs Sun
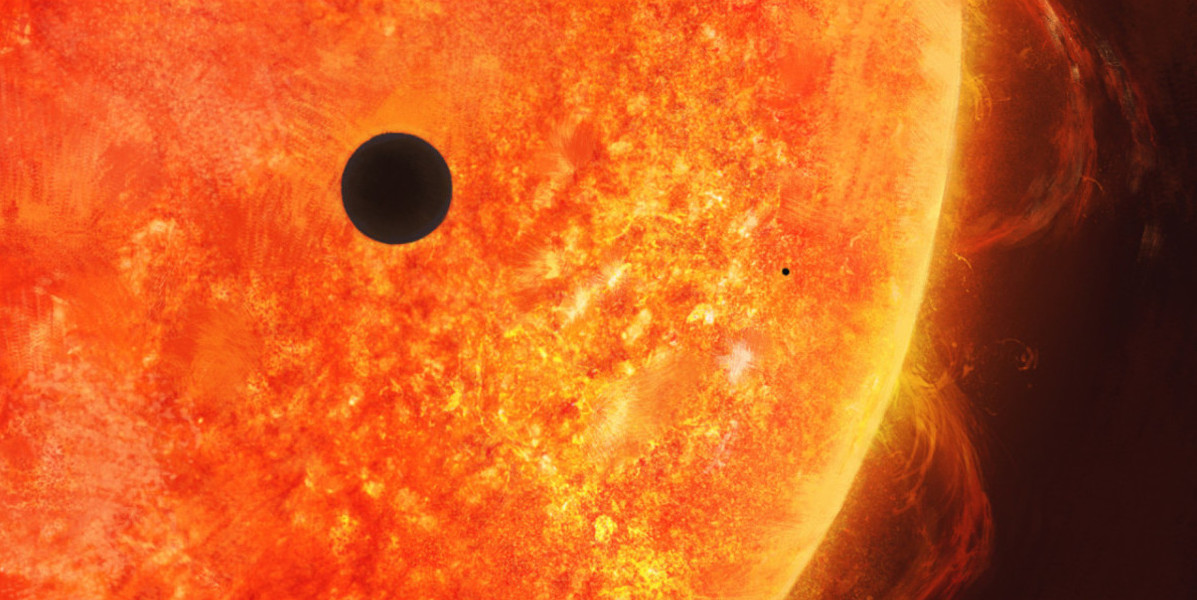

Mercury vs sun – Mercury and the Sun are vastly different celestial bodies, with striking disparities in their physical attributes. Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun, is a small, rocky world, while the Sun is an enormous, glowing ball of hot plasma.
While Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun, is known for its rapid orbit, the Sun, on the other hand, captivates with its immense size and gravitational pull. To catch the latest updates on the partido de venezuela hoy en vivo, click here: partido de venezuela hoy en vivo.
Returning to our celestial comparison, Mercury’s surface temperature can reach extremes, while the Sun’s core is a raging inferno.
Size, Mass, and Density
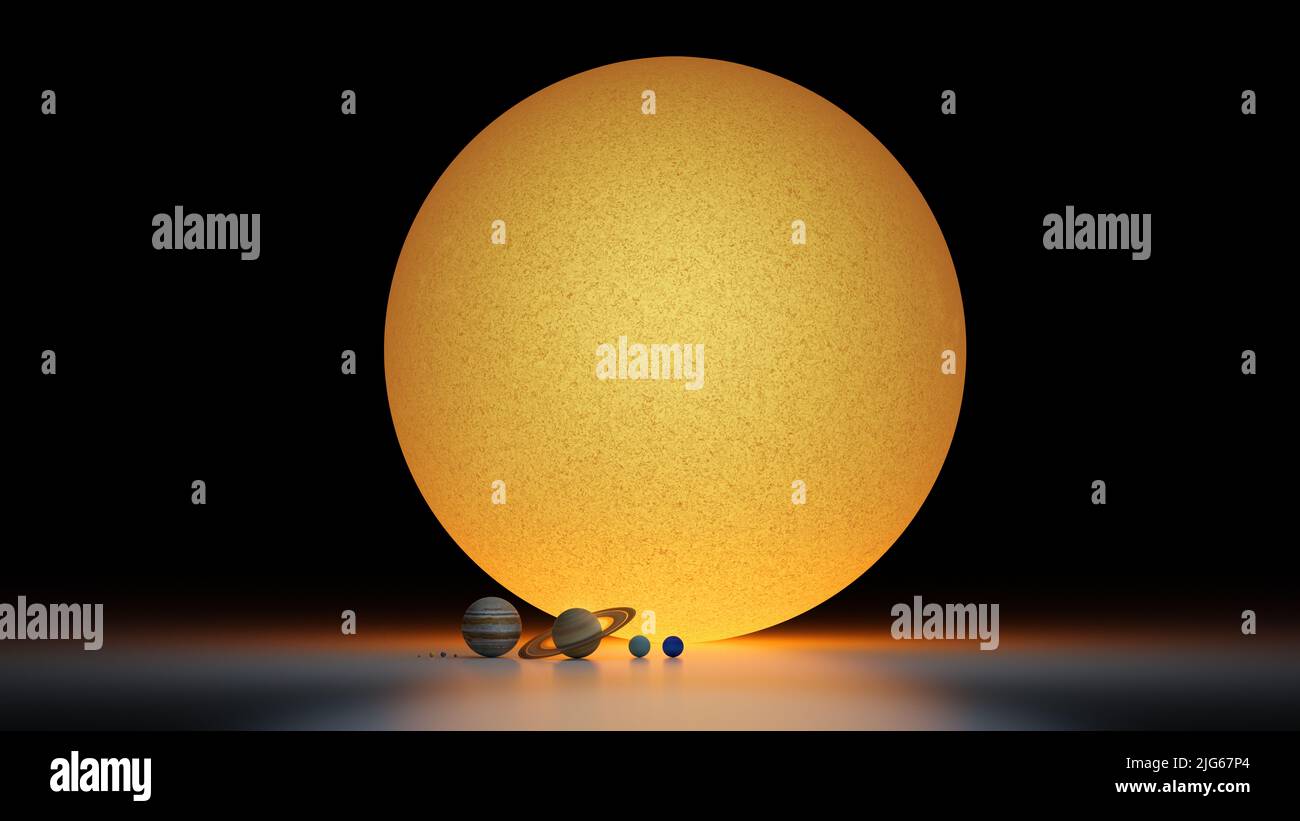
- Size: The Sun is over 100 times larger than Mercury in diameter, with a volume approximately 1.3 million times greater.
- Mass: The Sun’s mass is approximately 330,000 times that of Mercury, making it the dominant gravitational force in our solar system.
- Density: Mercury has a density of about 5.4 grams per cubic centimeter, while the Sun’s density is only 1.4 grams per cubic centimeter, indicating the Sun’s gaseous nature.
Surface Temperatures and Compositions
The Sun’s surface temperature reaches an astounding 5,778 Kelvin (5,505 degrees Celsius), emitting vast amounts of energy as sunlight. In contrast, Mercury’s surface temperature varies drastically, ranging from extreme heat on the sunlit side (up to 450 degrees Celsius) to frigid cold on the dark side (-180 degrees Celsius). This temperature difference is due to Mercury’s lack of an atmosphere to retain heat.
Mercury is primarily composed of iron and silicate minerals, while the Sun is composed almost entirely of hydrogen and helium gas.
The vast difference between the searing heat of the sun and the cool, liquid nature of mercury is a stark reminder of the diverse forces at play in our universe. Just as the sun’s fiery embrace illuminates our world, so too can the electrifying energy of venezuela vs jamaica en vivo captivate our senses.
Yet, amidst the celestial spectacle, the subtle dance of mercury, ever-changing and elusive, reminds us of the delicate balance that governs all things.
Atmospheres and Magnetic Fields, Mercury vs sun
Mercury has an extremely thin atmosphere, primarily composed of helium and oxygen. The Sun, on the other hand, has a vast, extended atmosphere called the corona, which extends millions of kilometers into space.
Mercury possesses a weak magnetic field, while the Sun’s magnetic field is extremely powerful and complex, shaping the solar wind and protecting the Earth from harmful solar radiation.
Orbital Properties
Mercury and the Sun exhibit distinct orbital characteristics that shape their celestial dance within our solar system.
Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun, orbits our star in an elliptical path with a period of approximately 88 Earth days. Its average distance from Earth varies between 77 million kilometers at its closest point (perihelion) and 121 million kilometers at its farthest point (aphelion).
Orbital Resonance
Mercury’s orbit is unique due to its 3:2 orbital resonance with the Sun. This means that Mercury completes three orbits around the Sun for every two orbits completed by Venus, the planet neighboring it. This resonance stabilizes Mercury’s orbit and prevents it from becoming too eccentric.
The Sun as the Center of the Solar System
The Sun, the colossal star at the heart of our solar system, exerts a gravitational pull on all the planets within its domain. This gravitational influence dictates the orbits of the planets, keeping them in a harmonious celestial ballet.
Solar System Impact
Mercury and the Sun play distinct roles in shaping our solar system’s formation and evolution. Mercury’s gravitational influence stabilizes the inner solar system, while the Sun’s energy drives the climate and habitability of Earth and other planets.
Mercury’s Role in Stabilizing the Inner Solar System
Mercury’s eccentric orbit and proximity to the Sun have a stabilizing effect on the inner solar system. Its gravitational pull helps prevent collisions between asteroids and planets, particularly in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. This stabilizing effect has been crucial in preserving the stability and order of the inner solar system over billions of years.
The Sun’s Influence on Climate and Habitability
The Sun’s immense energy output, primarily in the form of electromagnetic radiation, is the driving force behind the climate and habitability of Earth and other planets. The Sun’s energy warms the Earth’s surface, drives weather patterns, and supports the growth of life. The Sun’s radiation also interacts with Earth’s atmosphere, creating the ozone layer that protects life from harmful ultraviolet rays. Without the Sun’s energy, Earth would be a frozen, lifeless planet.